BLOG
ブログ
BLOG
Ethereum: Is there a limit to how much extra data can be put into blocks via scripts?
Ethereum Block Data Limit: Understanding the Scripting Mechanism
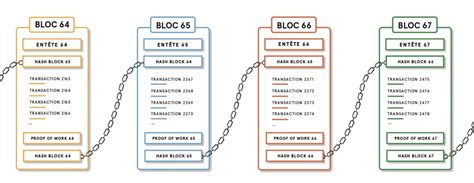
Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain platform that enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). One of the key features that sets Ethereum apart from other blockchain platforms is its scripting mechanism. This allows miners to add additional data to blocks that can be used for various purposes, such as verifying transactions, processing events, or even staking.
In this article, we will delve into the Ethereum block data limit and examine how much a miner can add.
Understanding Ethereum Scripting
Ethereum’s scripting mechanism is based on Solidity, a programming language that allows developers to create smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the contract written directly into lines of code. In Ethereum, smart contracts are stored on the blockchain and executed by miners when new blocks are created.
When a miner creates a block, they can add additional data to it in the form of scripts. These scripts can be used for a variety of purposes, such as:
- Transaction Validation: Scripts can validate transactions and ensure that they meet required conditions.
- Event Handling: Scripts can handle events such as the creation or update of smart contracts or other blockchain-related events.
- Staking: Scripts can be used to stake cryptocurrency, allowing users to participate in the validation process.
Limits on Additional Data
While Ethereum’s scripting engine is powerful and flexible, there are limits to how much additional data a miner can add. These limits are set by the Ethereum protocol and enforced by the mining community.
According to the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) specifications, each block can contain up to 1,500 bytes of additional data. This means that miners can add a maximum of 1,500 characters of additional data to a block before the block is considered invalid.
In practice, this limit translates to around 250-300 lines of code. Any script longer than 250-300 lines will likely be rejected by the Ethereum network and considered too large to execute.
How much extra data can be added?
While there are limits to how much extra data a miner can add, it is not impossible to exceed these limits. However, exceeding these limits can result in the rejection of a block or even the entire transaction.
To give you an idea of how long this limit is, consider the following example:
- A script that defines a complex smart contract with 100 lines of code can potentially exceed the 250-300 line limit.
- However, if the script is optimized and written in a way that minimizes its size, it can be rejected by the network.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while Ethereum’s scripting mechanism allows for some flexibility when it comes to additional data, there are limits to how much can be added. Miners can add up to 1,500 bytes of additional data to each block, which amounts to approximately 250-300 lines of code. While exceeding these limits can result in rejection or even the entire transaction, it is not impossible.
If you are considering creating a smart contract on Ethereum that requires a large amount of additional data, you will need to keep the limitations in mind and optimize your script accordingly.
